Join Us On Social Media!
2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
46 Posts · 8 Followers · 39 Photos · 153 Likes
Began 6 months ago by
Follow This Thread
Not currently following
> Click to follow
> Click to follow
Latest Post 5 months ago by
( Newest Posts Shown First )
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
21 Views · 2 Likes
Country: 🇮🇹 Italy
Online: 4 minutes ago
Online: 4 minutes ago
Hi Doug, thanks so much for your reply.
You're right.
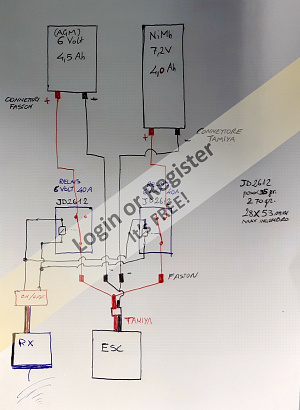
Only one relay of this type is enough. The second is useless.
I redid the drawing.
The question was in message #35.
I didn't translate all the parts of your reply correctly, but I get the general gist.
The diode on the coil is absolutely necessary (unfortunately, I know the reasons why it needs to be there). You're right about that too, thank you so much for reminding me.
Regarding the sentence: "Most importantly, the coil energizes at 6 volts and can handle 40 amps."
It's clear, there's no doubt about it; the 40 amps certainly don't refer to the current flowing through the coil.
Very little current flows through the coil; in fact, it's managed by another circuit (the on-off switch that manages a low current). Moreover, those coils have very thin filaments.
The 6 volts refer to the coil's excitation voltage, and the 40 amperes refer to the current flowing through the switch controlled by the coil.
Sorry, I took that for granted.
Thanks also for the invaluable advice on the relay type. This certainly avoids the need for a second relay.
Do you think the relay I linked is "Break before make"? I think so, but I haven't been able to figure it out.
I wanted to ask if the circuit is OK as it is (see the new attached drawing), but more importantly, if this relay is correct, or which relay you would choose.
Could you tell me (if you don't have a reference model or type) just the general specifications?
You're right.
Only one relay of this type is enough. The second is useless.
I redid the drawing.
The question was in message #35.
I didn't translate all the parts of your reply correctly, but I get the general gist.
The diode on the coil is absolutely necessary (unfortunately, I know the reasons why it needs to be there). You're right about that too, thank you so much for reminding me.
Regarding the sentence: "Most importantly, the coil energizes at 6 volts and can handle 40 amps."
It's clear, there's no doubt about it; the 40 amps certainly don't refer to the current flowing through the coil.
Very little current flows through the coil; in fact, it's managed by another circuit (the on-off switch that manages a low current). Moreover, those coils have very thin filaments.
The 6 volts refer to the coil's excitation voltage, and the 40 amperes refer to the current flowing through the switch controlled by the coil.
Sorry, I took that for granted.
Thanks also for the invaluable advice on the relay type. This certainly avoids the need for a second relay.
Do you think the relay I linked is "Break before make"? I think so, but I haven't been able to figure it out.
I wanted to ask if the circuit is OK as it is (see the new attached drawing), but more importantly, if this relay is correct, or which relay you would choose.
Could you tell me (if you don't have a reference model or type) just the general specifications?

▲
⟩⟩
hermank
stevedownunder
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
24 Views · 6 Likes
Country: 🇩🇪 Germany
Online: 3 days ago
Online: 3 days ago
Sorry Alessandro, Re 'I wanted to return to my question.' But what was your question?
Also can you explain what exactly you are trying to do and why you are wasting an unnecessary relay on the right in your wiring diagrams? Also you are wasting the NO contact in the one left in the diagram. Why the heck do you need 6 contacts? And why 20A?
BTW: the relay coil connections do not count to the number of relay contacts!
To switch batteries, or any other sources or loads, you should only need a single relay of single pole double throw type. Also make sure it is a 'Break before make' type, in order to avoid your fear of connecting the positive terminals of both batteries together.
To whit "What I'm not convinced by this scheme is the simultaneous mechanical action of the coils, especially because the batteries have different potentials and for a few moments I run the risk of them being closed in parallel. In that case, current would flow between them, with harmful effects."
Re; "most importantly, the coil energizes at 6 volts and can handle 40 amps."
I assume a translation problem here - the relay coil is unlikely to need more than 1A and has nothing to do with the contact rating, i.e. the maximum load current that the relay can reliably transfer without burning the contacts.
BTW: You WILL need some diodes!
Simple signal type diodes (max 1A) across the relay coils to suppress the back EMF pulse created when the relay coil switches off, which otherwise can destroy the output transistor of the switching device.
Doug 😎
Also can you explain what exactly you are trying to do and why you are wasting an unnecessary relay on the right in your wiring diagrams? Also you are wasting the NO contact in the one left in the diagram. Why the heck do you need 6 contacts? And why 20A?
BTW: the relay coil connections do not count to the number of relay contacts!
To switch batteries, or any other sources or loads, you should only need a single relay of single pole double throw type. Also make sure it is a 'Break before make' type, in order to avoid your fear of connecting the positive terminals of both batteries together.
To whit "What I'm not convinced by this scheme is the simultaneous mechanical action of the coils, especially because the batteries have different potentials and for a few moments I run the risk of them being closed in parallel. In that case, current would flow between them, with harmful effects."
Re; "most importantly, the coil energizes at 6 volts and can handle 40 amps."
I assume a translation problem here - the relay coil is unlikely to need more than 1A and has nothing to do with the contact rating, i.e. the maximum load current that the relay can reliably transfer without burning the contacts.
BTW: You WILL need some diodes!
Simple signal type diodes (max 1A) across the relay coils to suppress the back EMF pulse created when the relay coil switches off, which otherwise can destroy the output transistor of the switching device.
Doug 😎
▲
⟩⟩
hermank
roycv
SimpleSailor
AlessandroSPQR
thadlietz
stevedownunder
Young at heart 😉 Slightly older in other places.😊 Cheers Doug
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
24 Views · 2 Likes
Country: 🇮🇹 Italy
Online: 4 minutes ago
Online: 4 minutes ago
Good evening everyone, after the long discussion about AGM batteries, I wanted to return to my question.
If you don't want to read the entire message because it's too long, you can read the questions at the end and, if you'd like, give me your opinion and advice.
I confirm that mechanical switches that support large currents are too large (at least I haven't found any) and, I must say, also very expensive.
I found some relays that might be suitable for my needs.
One is the Bosch JD2912 DC relay (I'm attaching the technical specifications for anyone interested) or similar.
It's very compact and weighs just 35 grams, but, most importantly, the coil energizes at 6 volts and can handle 40 amps.
The only problem is that it only has five contacts. Since two of the contacts are for the coil, three remain for just one contact.
To switch from one battery to another, I need more contacts.
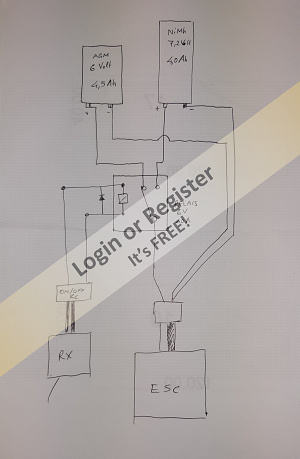
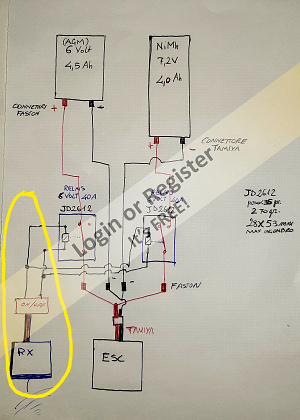
I thought that with two relays I should be able to switch from one battery to the other according to this scheme (see drawing no. 1).
I don't like it very much; I would have preferred a single relay with multiple N/O or N/C contacts.
What I'm not convinced by this scheme is the simultaneous mechanical action of the coils, especially because the batteries have different potentials and for a few moments I run the risk of them being closed in parallel. In that case, current would flow between them, with harmful effects.
In other words, I'm not sure that the opening of one circuit and the closing of the other would occur simultaneously. This wouldn't happen with a single coil controlling all the contacts.
Actually, in another circuit I made to switch the power supply from a 6-volt battery to a 12-volt one (with the same ESC that only supported 8.4 volts), I had no problems, even though I used multiple identical relays (unsoldered and recovered from the same board).
When operating the remote control stick (throttle) beyond a certain limit, the direct circuit from the 12-volt battery kicked in (bypassing the ESC, which was therefore not damaged).
The coil's excitation threshold was only reached with the throttle stick fully depressed because I had created voltage drops on the line that prevented the coil from exciting with lower voltages (supplied by the ESC with the stick in intermediate positions).
However, despite this positive experience, I'd rather not take the risk.
I'd prefer to use a single relay because the switching would certainly be instantaneous and simultaneous.
But I need to find the right relay; so far I haven't found one and I don't even know if it exists.
The current to the relay excitation coils can be controlled by an RC on-off switch (which I already have). In this case, I can draw the current directly from the receiver (as in the second attached drawing, yellow outline) or draw it from a 6-volt battery using another type of double-wire on-off switch (which I also already have).
Do you think the circuit would work?
I wanted to ask if you've ever used or found online 6-volt relays with multiple switching contacts (at least 6) capable of handling at least 20 amps.
I've also considered adding a diode, but I'm still trying to decide.
I've found ones with a low voltage drop (Schottky diodes), but I can't find any that can handle high currents.

If you don't want to read the entire message because it's too long, you can read the questions at the end and, if you'd like, give me your opinion and advice.
I confirm that mechanical switches that support large currents are too large (at least I haven't found any) and, I must say, also very expensive.
I found some relays that might be suitable for my needs.
One is the Bosch JD2912 DC relay (I'm attaching the technical specifications for anyone interested) or similar.
It's very compact and weighs just 35 grams, but, most importantly, the coil energizes at 6 volts and can handle 40 amps.
The only problem is that it only has five contacts. Since two of the contacts are for the coil, three remain for just one contact.
To switch from one battery to another, I need more contacts.
I thought that with two relays I should be able to switch from one battery to the other according to this scheme (see drawing no. 1).
I don't like it very much; I would have preferred a single relay with multiple N/O or N/C contacts.
What I'm not convinced by this scheme is the simultaneous mechanical action of the coils, especially because the batteries have different potentials and for a few moments I run the risk of them being closed in parallel. In that case, current would flow between them, with harmful effects.
In other words, I'm not sure that the opening of one circuit and the closing of the other would occur simultaneously. This wouldn't happen with a single coil controlling all the contacts.
Actually, in another circuit I made to switch the power supply from a 6-volt battery to a 12-volt one (with the same ESC that only supported 8.4 volts), I had no problems, even though I used multiple identical relays (unsoldered and recovered from the same board).
When operating the remote control stick (throttle) beyond a certain limit, the direct circuit from the 12-volt battery kicked in (bypassing the ESC, which was therefore not damaged).
The coil's excitation threshold was only reached with the throttle stick fully depressed because I had created voltage drops on the line that prevented the coil from exciting with lower voltages (supplied by the ESC with the stick in intermediate positions).
However, despite this positive experience, I'd rather not take the risk.
I'd prefer to use a single relay because the switching would certainly be instantaneous and simultaneous.
But I need to find the right relay; so far I haven't found one and I don't even know if it exists.
The current to the relay excitation coils can be controlled by an RC on-off switch (which I already have). In this case, I can draw the current directly from the receiver (as in the second attached drawing, yellow outline) or draw it from a 6-volt battery using another type of double-wire on-off switch (which I also already have).
Do you think the circuit would work?
I wanted to ask if you've ever used or found online 6-volt relays with multiple switching contacts (at least 6) capable of handling at least 20 amps.
I've also considered adding a diode, but I'm still trying to decide.
I've found ones with a low voltage drop (Schottky diodes), but I can't find any that can handle high currents.



▲
⟩⟩
hermank
stevedownunder
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
34 Views · 2 Likes
Country: 🇮🇹 Italy
Online: 4 minutes ago
Online: 4 minutes ago
Hi Roy, there are hundreds of models and types of AGM batteries.
Furthermore, other non-AGM VRLA types, even more expensive ones, have different and often better characteristics.
Furthermore, other non-AGM VRLA types, even more expensive ones, have different and often better characteristics.
▲
⟩⟩
hermank
RodC
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
35 Views · 2 Likes
Country: 🇬🇧 United Kingdom
Online: 2 hours ago
Online: 2 hours ago
Hello Alessandro, I thought there maybe a new perhaps lighter and better SLA battery around.
I have used Cyclon cells, lead acid, but very similar in actual discharge capacity to NiMh cells. They do not seem to be around much any more.
These are AGM (Absorbed Glass Matte) but measured at the 5 hour rate as NiMh cells are. The SLA batteries are measured at the 20 hour rate.
Roy
I have used Cyclon cells, lead acid, but very similar in actual discharge capacity to NiMh cells. They do not seem to be around much any more.
These are AGM (Absorbed Glass Matte) but measured at the 5 hour rate as NiMh cells are. The SLA batteries are measured at the 20 hour rate.
Roy
▲
⟩⟩
hermank
RodC
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
34 Views · 3 Likes
Country: 🇮🇹 Italy
Online: 4 minutes ago
Online: 4 minutes ago
Hi Roy, you're right, my answer to your question could be labeled TLDR; however, if you notice, the first part (divided by the series of dashes) is very short and succinct.
For the second part, I myself advised that the rest could be skipped.
The following section shows that the batteries I used are VRLA AGM, and there are general indications on the technology used and the differences between the various technologies.
In reality, the batteries I use (I don't only use FIAMM; I've used that brand as an example for a concrete reference) are SLA (hence VRLA) as you say, but more precisely, VRLA AGM.
SLA is another way of calling VRLA.
Since AGMs are a subfamily of VRLAs, I'll just call them AGM (an AGM is still a VRLA, which is still a lead-acid battery).
Saying that the batteries I use are lead-acid isn't wrong, saying they're VRLA (or SLA) isn't wrong, but calling them AGM is more accurate.
If you look closely (see the attachments), the FG batteries I mentioned and used are also AGM. The manufacturer itself writes and calls them VRLA and AGM.
I understand your point, Roy. AGM batteries, like all lead-acid ones, have the major disadvantage of weight, but if you no longer use them and don't intend to use them, I don't understand why you asked me where to find them.
Even though I was looking for advice and opinions on a mechanical switch (to switch from one battery to another), I'm very happy that the discussion has shifted to AGM batteries, because many people are still confused.
I'm pleased that the terms defining the various technologies (flooded lead, VRLA AGM, VRLA gel, etc., etc.) have been clarified.
Many continue to see, read, and comment about AGM batteries without knowing they're AGM. Or they think AGMs are only used for start-stop systems in cars.
For this, I have to thank Roy for reopening a topic I'd already discussed.
In fact, these AGM batteries I use, which are indeed very small, are nothing new; they've been around for quite some time, and we've discussed them in many build blog and forum threads. I'm always happy to revisit these technical topics.

For the second part, I myself advised that the rest could be skipped.
The following section shows that the batteries I used are VRLA AGM, and there are general indications on the technology used and the differences between the various technologies.
In reality, the batteries I use (I don't only use FIAMM; I've used that brand as an example for a concrete reference) are SLA (hence VRLA) as you say, but more precisely, VRLA AGM.
SLA is another way of calling VRLA.
Since AGMs are a subfamily of VRLAs, I'll just call them AGM (an AGM is still a VRLA, which is still a lead-acid battery).
Saying that the batteries I use are lead-acid isn't wrong, saying they're VRLA (or SLA) isn't wrong, but calling them AGM is more accurate.
If you look closely (see the attachments), the FG batteries I mentioned and used are also AGM. The manufacturer itself writes and calls them VRLA and AGM.
I understand your point, Roy. AGM batteries, like all lead-acid ones, have the major disadvantage of weight, but if you no longer use them and don't intend to use them, I don't understand why you asked me where to find them.
Even though I was looking for advice and opinions on a mechanical switch (to switch from one battery to another), I'm very happy that the discussion has shifted to AGM batteries, because many people are still confused.
I'm pleased that the terms defining the various technologies (flooded lead, VRLA AGM, VRLA gel, etc., etc.) have been clarified.
Many continue to see, read, and comment about AGM batteries without knowing they're AGM. Or they think AGMs are only used for start-stop systems in cars.
For this, I have to thank Roy for reopening a topic I'd already discussed.
In fact, these AGM batteries I use, which are indeed very small, are nothing new; they've been around for quite some time, and we've discussed them in many build blog and forum threads. I'm always happy to revisit these technical topics.

▲
⟩⟩
hermank
RodC
roycv
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
37 Views · 4 Likes
Country: 🇬🇧 United Kingdom
Online: 2 hours ago
Online: 2 hours ago
There is nothing personal here for you, I was surprised the new technology in batteries had gone into small batteries.
I just wondered how many members of this forum were aware of the batteries now in their cars.
I mentioned my experience, there was nothing in there for you, or about you, Alessandro.
I Googled the battery you mentioned and read the technical details. I note the FG graded batteries are referred to as SLA in their own literature. Apparently similar to the good quality batteries we get Yuasa etc.
Personally, I stopped using SLA batteries some years ago as the weight to power ratio was unfavourable compared with NiMh batteries. I do not like LiPo cells but that is just my opinion.
Experience also tells me that long documents frequently get the initials TLDR.
Best regards
Roy
I just wondered how many members of this forum were aware of the batteries now in their cars.
I mentioned my experience, there was nothing in there for you, or about you, Alessandro.
I Googled the battery you mentioned and read the technical details. I note the FG graded batteries are referred to as SLA in their own literature. Apparently similar to the good quality batteries we get Yuasa etc.
Personally, I stopped using SLA batteries some years ago as the weight to power ratio was unfavourable compared with NiMh batteries. I do not like LiPo cells but that is just my opinion.
Experience also tells me that long documents frequently get the initials TLDR.
Best regards
Roy
▲
⟩⟩
hermank
RodC
stevedownunder
RNinMunich
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
37 Views · 3 Likes
Country: 🇮🇹 Italy
Online: 4 minutes ago
Online: 4 minutes ago
Hi Roy, I think you're a bit off track.
You wrote:
"Cars with stop/start function have to use a different battery than the standard type battery and cost twice as much."
Well, I never actually said I used batteries for the start/stop function of cars.
I explained to you in detail which batteries I use (including their dimensions) and, to avoid any misunderstandings, I also included photos.
I then told you where I get the batteries I use, not others I don't have. Certainly not the ones for the start/stop function of cars, which I don't use for my boats.
Also, I never said I used EFBs.
In short, I didn't understand the meaning or connection of your last message with my answer. I immediately thought it was a translation error and reread your question and my answer several times.
You asked me:
"I didn't know you can buy small Absorbent Glass Matte batteries?"
and I showed you the ones I use; I wrote down the dimensions. I'll leave it up to you to decide if they're small.
Then you informed me you have one in your car.
Okay, fine, but I don't know it; I can tell you about mine, not the ones I don't use.
Finally, you asked me where to find them, and I answered "where I find mine," obviously not the one you're referring to.
I'm sure I understood your question correctly and answered it correctly, but I could be wrong, so if there's anything unclear (I'm sure I explained myself poorly) or you have any other questions, please let me know; I'll be happy to answer.
You wrote:
"Cars with stop/start function have to use a different battery than the standard type battery and cost twice as much."
Well, I never actually said I used batteries for the start/stop function of cars.
I explained to you in detail which batteries I use (including their dimensions) and, to avoid any misunderstandings, I also included photos.
I then told you where I get the batteries I use, not others I don't have. Certainly not the ones for the start/stop function of cars, which I don't use for my boats.
Also, I never said I used EFBs.
In short, I didn't understand the meaning or connection of your last message with my answer. I immediately thought it was a translation error and reread your question and my answer several times.
You asked me:
"I didn't know you can buy small Absorbent Glass Matte batteries?"
and I showed you the ones I use; I wrote down the dimensions. I'll leave it up to you to decide if they're small.
Then you informed me you have one in your car.
Okay, fine, but I don't know it; I can tell you about mine, not the ones I don't use.
Finally, you asked me where to find them, and I answered "where I find mine," obviously not the one you're referring to.
I'm sure I understood your question correctly and answered it correctly, but I could be wrong, so if there's anything unclear (I'm sure I explained myself poorly) or you have any other questions, please let me know; I'll be happy to answer.
▲
⟩⟩
hermank
RodC
stevedownunder
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
38 Views · 4 Likes
Country: 🇬🇧 United Kingdom
Online: 2 hours ago
Online: 2 hours ago
Thanks for the detail.
Cars with stop/start function have to use a different battery to the standard type battery and cost twice as much.
Quote:-
One technicality though, a normal lead acid battery cannot run this system, so special batteries are needed: Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB).
The EFB batteries are for the larger cars altough also work for smaller cars.
Other information I have come across requires a special charger with a lower cut off voltage for the charge voltage.
I got into this as I had an old battery monitor from my last car which I plugged in to my current car and it said I need to re-new my battery.
But apparently the battery voltage is limited to 13 volts for the advanced batteries but the old lead acid batteries are allowed to have 2.4 volts per cell i.e. 14.4 volts on full charge.
Confusing? Yes but with 60% of the cars in Europe on S/S need these batteries.
Roy
Cars with stop/start function have to use a different battery to the standard type battery and cost twice as much.
Quote:-
One technicality though, a normal lead acid battery cannot run this system, so special batteries are needed: Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB).
The EFB batteries are for the larger cars altough also work for smaller cars.
Other information I have come across requires a special charger with a lower cut off voltage for the charge voltage.
I got into this as I had an old battery monitor from my last car which I plugged in to my current car and it said I need to re-new my battery.
But apparently the battery voltage is limited to 13 volts for the advanced batteries but the old lead acid batteries are allowed to have 2.4 volts per cell i.e. 14.4 volts on full charge.
Confusing? Yes but with 60% of the cars in Europe on S/S need these batteries.
Roy
▲
⟩⟩
hermank
RNinMunich
stevedownunder
RodC
📝 2nd voyage on Lake Paterno of the 1:60 scale model of a schooner-armed steam gunboat, assisted by a
38 Views · 5 Likes
Country: 🇮🇹 Italy
Online: 4 minutes ago
Online: 4 minutes ago
Hi Roy.
The AGM batteries I used are those in the first three photos.
There are different voltages (V) and electrical charges (Ah) for this type of lead-acid battery.
For simplicity, I'll refer to the FIAMM brand.
I currently use three inexpensive models of this type:
1) the 6 Volt, 4.5 Ah (dimensions: 106 x 47 x 70 mm) that I used for RC ship models; see the fourth attached photo (FG 10451).
2) the 12 Volt, 7.2 Ah (dimensions 151 x 65 x 100 mm) that I used for my alarm control unit; see the fifth attached photo (FG 20721).
3) the 12 Volt, 2 Ah (dimensions 178 x 35 x 67 mm) that I used for my alarm's external siren; see the sixth attached photo. (FG 20201)
4) I recently replaced the batteries in the control unit and the external siren of my alarm (which I installed myself years ago). The batteries weren't meant to be thrown away, so I currently use them to power the remote controls. With a small modification, I avoid wasting eight 1.5-volt AA alkaline batteries, which are not rechargeable. See the seventh photo attached.
I know many people simply call these batteries lead-acid batteries.
The term isn't incorrect, but it's very generic.
For example, the batteries we use in common cars are lead-acid, but they contain liquid and can't be turned or flipped. The liquid can be refilled.
Another type of lead-acid battery is gel.
AGM (Absorbent Glass Material) batteries are part of the VRLA (valve regulated lead-acid) family.
I can't find them in auto parts stores or even regular electronics stores.
I can find them in large electronics stores or in shops specializing in alarm and video surveillance supplies.
I can also find them online (for example, in the RS catalog).
The above answers your question; you can skip reading the rest.
Wikipedia also provides a brief description of VRLA technology and explains the differences between AGM and Gel.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Copy/paste Wikipedia EN
A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery,[1] is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells.[2]
There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery).[3] Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other.[4]
Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM types of VRLA can be mounted in any orientation and do not require constant maintenance. The term "maintenance-free" is a misnomer, as VRLA batteries still require cleaning and regular functional testing. They are widely used in large portable electrical devices, off-grid power systems (including uninterruptible power systems), motor vehicles (as traction batteries for light electric vehicles such as golf carts and as starter or auxiliary batteries for heavier vehicles) and similar roles, where large amounts of storage are needed at a lower cost than other low-maintenance technologies like lithium ion.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Appendix. Some specific product features. This serves as an example to understand the others.
The Fiamm FG battery range is specifically designed for optimal performance and protection from electrical faults. The high-quality battery ensures no electrolyte leaks from the case or terminals. This battery requires virtually no maintenance thanks to its perfectly sealed structure and the recombination of gases within the cell.
This battery series uses a unique electrolyte suspension system incorporating a microfine glass mat (AGM) to retain the maximum amount of electrolyte in the cells.
Features and Benefits
Optimized for discharge up to 20 hours
5-year design life in flotation operations in a temperature-controlled environment
Gas recombination and VRLA AGM technology with 99% internal recombination
Spill-free and maintenance-free
Non-hazardous material for air/marine/rail/road transport
100% recyclable
Applications
Alarm systems
Communication equipment
Emergency lighting
Fire and security systems
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Differences between LEAD ACID and VRLA (AGM and GEL)
Lead acid batteries are made up of a set of cells composed of lead and sulfuric acid. These chemical elements allow the battery to produce electrical energy repeatedly and be continuously recharged. They were the first rechargeable batteries developed in over a century and still play an important role in the generation of energy for many machines today.
Lead acid batteries are chemically composed of lead and sulfuric acid; the term AGM stands for Absorbed Glass Mat, indicating that AGM technology batteries are internally composed of glass fibers that completely absorb the electrolyte, preventing it from flowing freely.
AGM batteries, also known as VRLA AGM batteries, are constructed as sealed lead-acid batteries. They have a plastic casing that makes them stable, watertight, and resistant to external agents. Even if the plastic casing were to break, there's no chance of acid leaking out because the electrolyte is permeated by the glass fibers.
It's reliable and can withstand oblique positions and strong vibrations without damage; these characteristics, among others, are what make AGM batteries so famous.
The hermetic seal, in addition to allowing the battery to be positioned anywhere, eliminates the need for replenishing the battery's liquid reserves, whether water or acid, as occurs with open batteries, specifically flooded lead-acid batteries and common starter batteries. This is because after each use, when the battery is recharged, the electrolyte solution within becomes available again within the glass fiber mesh, for a new reaction under the same physical and chemical conditions as before.
On this page, we find gel batteries, which are lead-acid batteries; That is, they have the chemical structure of a classic lead-acid battery, composed of lead and sulfuric acid, with the presence of another chemical component, silicic acid, which gives the electrolyte the consistency of a gelatinous liquid, hence the name GEL.
It might seem like a small difference, but this chemical characteristic, creating a different consistency in the electrolyte, triggers a specific chemical reaction in energy production. The gel electrolyte allows the battery to have greater resistance to acid, which determines differences in performance compared to other lead-acid batteries. Consequently, these differences also develop in discharge, in the battery's resistance to stress, and in its maintenance. Another factor is the internal construction of the battery separators, which allows it to function with both deep discharges and very shallow discharges.
The first characteristic resulting from the greater resistance of gel electrolyte to acid is its limited suitability for use when high starting currents are required, such as for starter motors. The particularity that makes it valuable is its resistance to deep discharge. Thanks to the gel electrolyte, they have high Ah capacities and a long expected design life. Gel batteries can be used cyclically and, while capable of recovering quickly from a discharge that is not very deep, they can also withstand deep discharges without suffering damage. They offer high capacity and recharge slowly. These are the main differences that make gel batteries preferable to AGM batteries.










The AGM batteries I used are those in the first three photos.
There are different voltages (V) and electrical charges (Ah) for this type of lead-acid battery.
For simplicity, I'll refer to the FIAMM brand.
I currently use three inexpensive models of this type:
1) the 6 Volt, 4.5 Ah (dimensions: 106 x 47 x 70 mm) that I used for RC ship models; see the fourth attached photo (FG 10451).
2) the 12 Volt, 7.2 Ah (dimensions 151 x 65 x 100 mm) that I used for my alarm control unit; see the fifth attached photo (FG 20721).
3) the 12 Volt, 2 Ah (dimensions 178 x 35 x 67 mm) that I used for my alarm's external siren; see the sixth attached photo. (FG 20201)
4) I recently replaced the batteries in the control unit and the external siren of my alarm (which I installed myself years ago). The batteries weren't meant to be thrown away, so I currently use them to power the remote controls. With a small modification, I avoid wasting eight 1.5-volt AA alkaline batteries, which are not rechargeable. See the seventh photo attached.
I know many people simply call these batteries lead-acid batteries.
The term isn't incorrect, but it's very generic.
For example, the batteries we use in common cars are lead-acid, but they contain liquid and can't be turned or flipped. The liquid can be refilled.
Another type of lead-acid battery is gel.
AGM (Absorbent Glass Material) batteries are part of the VRLA (valve regulated lead-acid) family.
I can't find them in auto parts stores or even regular electronics stores.
I can find them in large electronics stores or in shops specializing in alarm and video surveillance supplies.
I can also find them online (for example, in the RS catalog).
The above answers your question; you can skip reading the rest.
Wikipedia also provides a brief description of VRLA technology and explains the differences between AGM and Gel.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Copy/paste Wikipedia EN
A valve regulated lead‐acid (VRLA) battery, commonly known as a sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery,[1] is a type of lead-acid battery characterized by a limited amount of electrolyte ("starved" electrolyte) absorbed in a plate separator or formed into a gel, proportioning of the negative and positive plates so that oxygen recombination is facilitated within the cell, and the presence of a relief valve that retains the battery contents independent of the position of the cells.[2]
There are two primary types of VRLA batteries: absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel cell (gel battery).[3] Gel cells add silica dust to the electrolyte, forming a thick putty-like gel; AGM (absorbent glass mat) batteries feature fiberglass mesh between the battery plates, which serves to contain the electrolyte and separate the plates. Both types of VRLA batteries offer advantages and disadvantages compared to flooded vented lead-acid (VLA) batteries or each other.[4]
Due to their construction, the gel cell and AGM types of VRLA can be mounted in any orientation and do not require constant maintenance. The term "maintenance-free" is a misnomer, as VRLA batteries still require cleaning and regular functional testing. They are widely used in large portable electrical devices, off-grid power systems (including uninterruptible power systems), motor vehicles (as traction batteries for light electric vehicles such as golf carts and as starter or auxiliary batteries for heavier vehicles) and similar roles, where large amounts of storage are needed at a lower cost than other low-maintenance technologies like lithium ion.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Appendix. Some specific product features. This serves as an example to understand the others.
The Fiamm FG battery range is specifically designed for optimal performance and protection from electrical faults. The high-quality battery ensures no electrolyte leaks from the case or terminals. This battery requires virtually no maintenance thanks to its perfectly sealed structure and the recombination of gases within the cell.
This battery series uses a unique electrolyte suspension system incorporating a microfine glass mat (AGM) to retain the maximum amount of electrolyte in the cells.
Features and Benefits
Optimized for discharge up to 20 hours
5-year design life in flotation operations in a temperature-controlled environment
Gas recombination and VRLA AGM technology with 99% internal recombination
Spill-free and maintenance-free
Non-hazardous material for air/marine/rail/road transport
100% recyclable
Applications
Alarm systems
Communication equipment
Emergency lighting
Fire and security systems
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Differences between LEAD ACID and VRLA (AGM and GEL)
Lead acid batteries are made up of a set of cells composed of lead and sulfuric acid. These chemical elements allow the battery to produce electrical energy repeatedly and be continuously recharged. They were the first rechargeable batteries developed in over a century and still play an important role in the generation of energy for many machines today.
Lead acid batteries are chemically composed of lead and sulfuric acid; the term AGM stands for Absorbed Glass Mat, indicating that AGM technology batteries are internally composed of glass fibers that completely absorb the electrolyte, preventing it from flowing freely.
AGM batteries, also known as VRLA AGM batteries, are constructed as sealed lead-acid batteries. They have a plastic casing that makes them stable, watertight, and resistant to external agents. Even if the plastic casing were to break, there's no chance of acid leaking out because the electrolyte is permeated by the glass fibers.
It's reliable and can withstand oblique positions and strong vibrations without damage; these characteristics, among others, are what make AGM batteries so famous.
The hermetic seal, in addition to allowing the battery to be positioned anywhere, eliminates the need for replenishing the battery's liquid reserves, whether water or acid, as occurs with open batteries, specifically flooded lead-acid batteries and common starter batteries. This is because after each use, when the battery is recharged, the electrolyte solution within becomes available again within the glass fiber mesh, for a new reaction under the same physical and chemical conditions as before.
On this page, we find gel batteries, which are lead-acid batteries; That is, they have the chemical structure of a classic lead-acid battery, composed of lead and sulfuric acid, with the presence of another chemical component, silicic acid, which gives the electrolyte the consistency of a gelatinous liquid, hence the name GEL.
It might seem like a small difference, but this chemical characteristic, creating a different consistency in the electrolyte, triggers a specific chemical reaction in energy production. The gel electrolyte allows the battery to have greater resistance to acid, which determines differences in performance compared to other lead-acid batteries. Consequently, these differences also develop in discharge, in the battery's resistance to stress, and in its maintenance. Another factor is the internal construction of the battery separators, which allows it to function with both deep discharges and very shallow discharges.
The first characteristic resulting from the greater resistance of gel electrolyte to acid is its limited suitability for use when high starting currents are required, such as for starter motors. The particularity that makes it valuable is its resistance to deep discharge. Thanks to the gel electrolyte, they have high Ah capacities and a long expected design life. Gel batteries can be used cyclically and, while capable of recovering quickly from a discharge that is not very deep, they can also withstand deep discharges without suffering damage. They offer high capacity and recharge slowly. These are the main differences that make gel batteries preferable to AGM batteries.











▲
⟩⟩
EdW
stevedownunder
hermank
Ronald
RodC





 Fleet Admiral
Fleet Admiral Italy
Italy